Measuring CO2
How to monitor indoor air quality?
CO2 is a good indicator of indoor air quality. Elevated CO2 concentrations can indicate inadequate ventilation, potentially leading to discomfort and impaired cognitive function among occupants. Monitoring CO2 helps identify areas with insufficient fresh air exchange, allowing for timely adjustments to ventilation systems to enhance overall indoor comfort. Additionally, proper CO2 measurement aids in the early detection of potential issues, such as malfunctioning HVAC systems or the presence of indoor pollution sources, contributing to a healthier living or working environment. Regular CO2 monitoring aligns with energy efficiency goals by optimizing ventilation rates based on actual occupancy, promoting both occupant well-being and sustainable building practices.
The effects of CO2
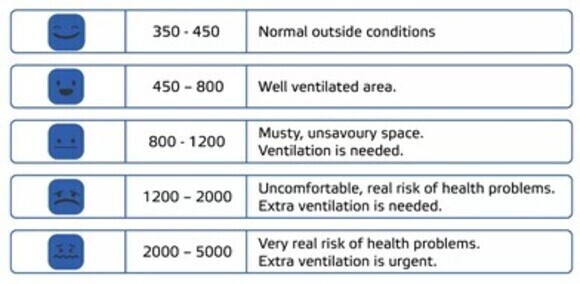
Moderate to high levels of carbon dioxide can cause headaches, reduced concentration and fatigue while higher concentrations can even produce nausea, dizziness and vomiting. Loss of consciousness can occur at extremely high concentrations. To prevent or reduce high concentrations of carbon dioxide in a building or room, fresh air should be supplied to the room.
Indoor CO2 levels constantly change, depending on the ventilation, the amount of people and the length of time they are present in an enclosed space. Indoor CO2 levels between 400-1.000 ppm are acceptable. When the values exceed this range, additional measures should be taken. This can be done by regularly replacing the air filters in indoor fan systems and installing a CO2 sensor to remind you when fresh air needs to enter the space.
