Why measure CO in underground parking garages?
In general, cars with combustion engines primarily emit carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon monoxide (CO) as exhaust gases. However, the relative amounts of each emitted gas can vary depending on several factors such as the type of fuel used, the efficiency of the engine, and the driving conditions. Due to their typically low ceiling, underground and enclosed car parks present a particular challenge to ventilation systems. Such a smart ventilation system must prevent the accumulation of toxic gases from motor exhausts in a garage. Toxic gas sensors are optimized to detect and measure these toxic gases in parking garages.
Typically, carbon dioxide (CO2) is emitted in larger quantities compared to carbon monoxide (CO) in combustion engine exhaust. This is because carbon dioxide is a byproduct of the complete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels such as gasoline or diesel. On the other hand, carbon monoxide is produced when there is incomplete combustion of fuel due to insufficient oxygen supply, inefficient combustion, or engine malfunction.
In terms of comparison, carbon dioxide emissions from combustion engines are generally much higher than carbon monoxide emissions. However, it's important to note that carbon monoxide is a more potent pollutant in terms of immediate health effects, as it can interfere with the body's ability to transport oxygen. Therefore, even though CO2 emissions are higher and therefore easier to detect, CO emissions are more concerning in terms of immediate health impacts. For this reason, CO sensors are sometimes prescribed in local regulations for monitoring air quality in parking garages. However, controlling a ventilation system in parking garages can be done much more efficiently based on CO2 measurements. When vehicles with combustion engines are active, CO2 sensors will be the first to detect poor air quality, long before the CO sensors notice increased values. Based on the CO2 measurement, the fans can be controlled to supply fresh air and remove toxic gases in a timely manner.
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide or CO is produced when combustion reactions are not fully completed, either through a lack of oxygen or due to low mixing. All combustion sources, including motor vehicles, power stations, waste incinerators, domestic gas boilers, and cookers, emit carbon monoxide.
The natural CO content in the ambient air is approximately 0,2 ppm (parts per million). Carbon monoxide affects the human respiratory system. CO attaches itself to red blood cells, preventing the uptake of oxygen. In the short term, this causes headaches and weariness. In the long term, this can cause brain damage even at relatively low concentrations. High concentrations of CO can cause physiological and pathological changes and even death. Since it is a colourless and odourless gas, it is often called the silent killer.
CO concentrations are typically highest in underground garages. CO rises, however, and can seep through to higher levels of buildings. There, it can chronically impact the inhabitants of apartments and office employees. Because the threat of death at high concentrations is real, it is very important to ventilate when CO concentrations rise. With Sentera CO sensor controllers, this can be done automatically.
Limit values for carbon monoxide
The World Health Organization has established reference values for concentrations and exposure times that are considered harmless for the entire population, including pregnant women and the elderly with (known or unknown) cardiovascular and respiratory problems:
10 mg/m³ (10 ppm) over the course of 8 hours.
30 mg/m³ (25 ppm) over the course of 1 hour.
60 mg/m³ (50 ppm) over the course of 30 min.
100 mg/m³ (90 ppm) over the course of 15 min.
Additionally, to combat long-term CO exposure, the organization NCBI recommends a limit of 7 mg/m³ (6 ppm) over a 24-hour period.
Carbon dioxide 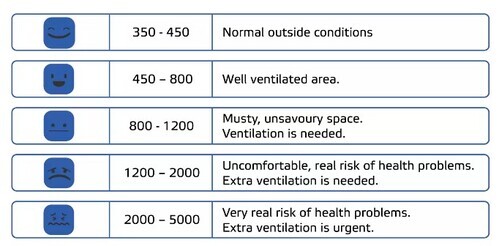

Carbon Dioxide or CO2 is a greenhouse gas that is natural and harmless in small quantities. It is necessary for the survival of life on earth. CO2 is not only the result from burning fossil fuels. Indoor carbon dioxide concentrations are the result of a combination of outdoor CO2, indoor breathing and the ventilation rate of the building. CO2 is evacuated by supplying fresh air.
The effects of CO2
Moderate to high levels of carbon dioxide can cause headaches, reduced concentration and fatigue while higher concentrations can even produce nausea, dizziness and vomiting. Loss of consciousness can occur at extremely high concentrations. To prevent or reduce high concentrations of carbon dioxide in an enclosed environment as an underground parking, fresh air should be supplied to wash away the carbon dioxide.
Indoor CO2 levels between 400-1.000 ppm are acceptable. When the values exceed this range, additional measures should be taken.
CO2 sensors are needed to guarantee good air quality in an underground parking garage. When vehicles with combustion engines are active, CO2 sensors will be the first to detect poor air quality, long before the CO sensors notice increased values. Based on the CO2 measurement, the fans can be controlled to supply fresh air and remove toxic gases in a timely manner.
