What is the purpose of the WEEE Directive?
What is WEEE?
WEEE stands for Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment and refers to discarded electrical and electronic products.
The amount of electronic waste generated each year in the EU is increasing rapidly. E-waste contains a complex mixture of materials, including hazardous substances that can cause serious environmental and health problems if not properly managed. At the same time, modern electronic products also contain valuable and often scarce resources, including critical raw materials. Many of these materials can be recovered, recycled, and reused.
WEEE Directive
The WEEE Directive (2012/19/EU) is an important European Union legal act designed to protect the environment and human health by reducing the negative impacts of electronic waste. It promotes the collection, recovery, recycling, and reuse of electrical and electronic equipment, helping to reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills.
By making manufacturers responsible for their products at the end of the lifecycle, the directive encourages better product design, supports sustainability, and contributes to the shift towards a circular economy, ultimately enhancing the EU’s strategic autonomy.
The main objectives of the WEEE directive are to:
- Prevent the production of WEEE wherever possible
- Promote reuse, recycling, and other forms of recovery of electrical and electronic waste
- Support efficient use of resources and the recovery of valuable secondary raw materials
Which products are covered by the WEEE Directive?
The directive applies to a broad range of electrical and electronic equipment, including:
- Household appliances (e.g. refrigerators, washing machines, microwaves)
- IT and telecommunications equipment (e.g. computers, phones, printers)
- Consumer electronics (e.g. televisions, radios, audio equipment)
- Lighting equipment (e.g. lamps and LED fixtures)
- Electrical tools (e.g. drills, saws)
- Medical and monitoring devices (with certain exemptions)
In general, most products that require electricity or batteries fall under the scope of the WEEE Directive.
What is the WEEE label and how must it be affixed?
The WEEE symbol is a crossed-out wheeled bin. It indicates that a product must not be disposed of with unsorted household waste, but must be taken to designated collection facilities for proper treatment.
The WEEE marking is mandatory for all electrical and electronic equipment placed on the EU market.
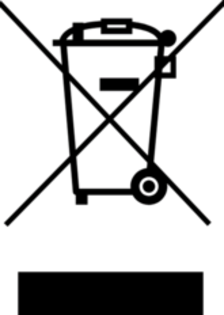
Products must display:
• The crossed-out wheeled bin symbol
• The producer’s identification mark (e.g. brand name or trademark)
For products placed on the market after 13 August 2005, one of the following must also be included:
• A solid bar underneath the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol, or
• The date on which the product was placed on the market
These markings must be permanent, clearly visible, and legible, and should be printed directly on the product.
Only if the product is too small or the marking would affect its function may the label be placed on the packaging, instructions for use, or warranty leaflet instead.
