What is the importance of measuring CO2?
What is CO2?
Carbon dioxide or CO2 is a colourless and odourless gas that is naturally present in our atmosphere. It plays an important role in the life on Earth as it is one of the main greenhouse gases, trapping heat in the atmosphere. Without these gases, the Earth would be too cold to support life.
However, human activities have dramatically increased the amount of CO2, disturbing the natural balance and leading to global warming and climate change.
Nowadays, outdoor air contains around 400 ppm. This concentration is considered normal and harmless to human and animals.
Carbon dioxide is also a natural by-product of both metabolic processes in living organisms and combustion. CO2 is released when fossil fuels — such as oil, gas, and coal — are burned. In addition, humans and animals exhale CO2 as they breathe, while plants extract CO2 from the air for photosynthesis and biomass production. In indoor spaces, including homes, schools, or offices, CO2 concentrations are the result of a combination of outdoor CO2, indoor breathing and the ventilation of the building.
Indicator of occupancy and air quality
Carbon dioxide is a reliable indicator of how many people are present in a room. Since most indoor CO2 derives from human metabolism, its concentration is closely linked to how intensively a space is being used. To maintain healthy indoor air quality and prevent CO2 build-up, it is important to ensure a constant supply of fresh air through proper ventilation.
Monitoring CO2 levels is therefore important because high concentrations indicate poor air quality. When CO2 levels rise, it often means that fresh air is running low and other pollutants — such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and airborne pathogens — may also be accumulating.
When an ill person uses a room, infectious airborne particles will be released, linger and accumulate — especially in poorly ventilated spaces. Although it is not feasible to measure all types of infectious particles directly, CO2 serves as a useful indicator. Higher CO2 levels often correlate with a higher risk of airborne disease transmission. By using CO2-based demand-controlled ventilation, the spread of disease from asymptomatic or pre-symptomatic individuals can be significantly reduced, as fresh air dilutes potentially harmful particles more effectively.
What are the effects of CO2?
Although CO2 is a normal component of the air we exhale, high levels can be harmful.
- Moderate to high levels can cause headaches, reduced concentration and fatigue.
- High concentrations can produce drowsiness, dizziness and vomiting.
- At extremely high concentrations, loss of consciousness can occur.
To prevent or reduce high concentrations of carbon dioxide in a building or room, fresh air should be supplied to the room.
Modern demand-controlled ventilation systems use CO2 sensors to assess whether additional fresh air is needed in a space. These systems automatically adjust ventilation based on real-time CO2 levels, ensuring optimal air quality that matches the number of occupants and their activity level.
CO2-controlled ventilation is especially useful in areas with variable occupancy, such as meeting rooms, classrooms, and university lecture halls.
Sentera offers a wide range of reliable CO2 sensors that can be integrated into these systems, making them a smart choice for effective and energy-efficient indoor climate control.
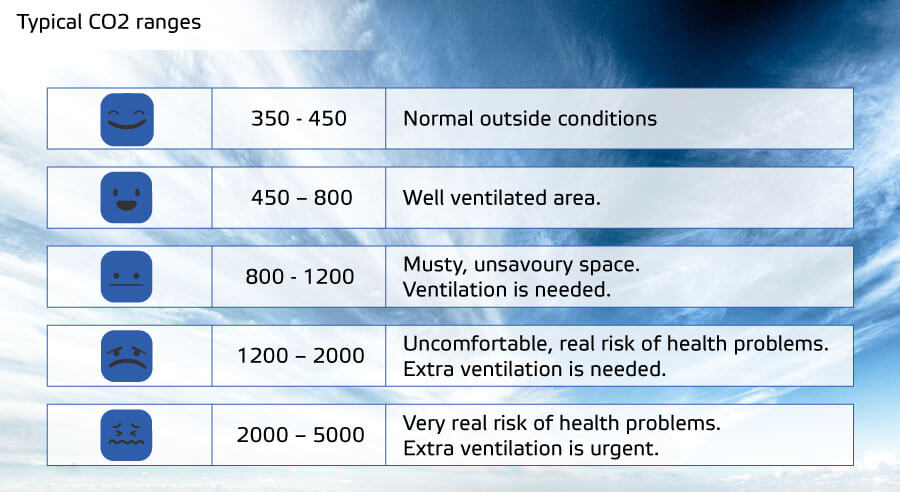
What are recommended CO2 levels?
Sentera CO2 sensors have adjustable detection ranges to suit various applications and can measure concentrations up to 10 000 ppm.
For typical indoor environments, it is recommended to keep CO2 concentrations below 800 ppm to maintain good air quality. Levels should not be forced below 400 ppm, as this is the average concentration of outdoor air.
In barns, CO2 must be exchanged with fresh air to keep concentrations as low as possible, for both animal and human safety. It is legally required that the CO2 concentration remains below 3000 ppm.
In greenhouses, by contrast, CO2 must be supplied to support plant growth. Plants perform optimally when CO2 levels are maintained between 400 and 1000 ppm.